Resume screening is one of the earliest decision points in the hiring process. Before interviews, assessments, or offers, organizations decide which candidates are even considered. That decision is shaped largely by how resumes are parsed and screened.
As hiring volumes increase and roles become more specialized, manual resume screening has become difficult to sustain. Resume parsing was introduced to reduce this burden by converting resumes into structured data that hiring teams could work with more efficiently. Over time, advances in artificial intelligence have changed how parsing and screening operate, particularly in terms of accuracy and consistency.
This article explains what resume parsing is, how it works, where traditional approaches fall short, and how AI-driven screening improves accuracy when implemented as part of a broader talent acquisition system.
What Is Resume Parsing
Resume parsing is the process of extracting information from resumes and converting it into structured, searchable data.
Most parsing systems identify and organize information such as:
- Personal details, including name and contact information
- Work experience, such as job titles, employers, and duration
- Educational background and qualifications
- Skills, certifications, and proficiencies
- Additional details like languages or professional summaries
Parsed data is typically stored inside an Applicant Tracking System (ATS), allowing recruiters to search, filter, and compare candidates without manually reviewing every resume. Instead of working with static documents, hiring teams work with standardized records that can be evaluated consistently across roles.
The primary goal of resume parsing is to reduce administrative effort and improve consistency at the earliest stage of the hiring process.
How Resume Parsing Works
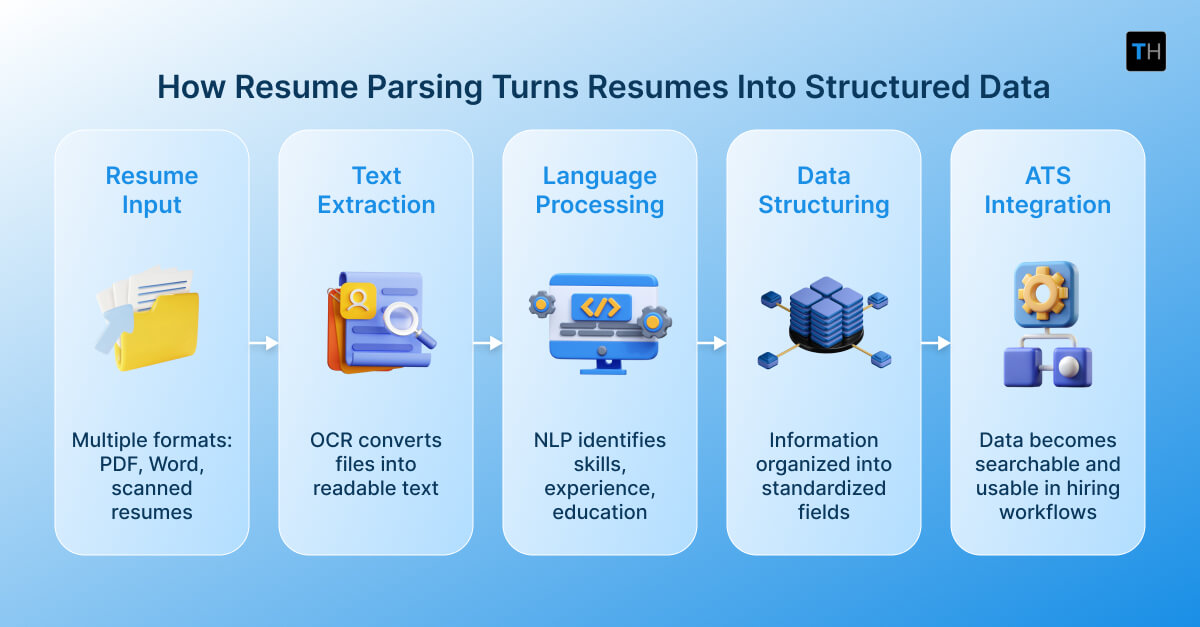
Although implementations vary, most resume parsing tools follow a similar process.
First, resumes submitted in formats such as PDF, Word, or scanned documents are converted into machine-readable text. Optical Character Recognition (OCR) is often used when resumes are not text-based.
Next, the text is processed using Natural Language Processing (NLP). NLP techniques analyze sentence structure and language patterns to identify entities such as skills, job titles, dates, and organizations.
Finally, the extracted information is organized into structured formats like JSON or XML and imported into the ATS or HR system. Recruiters can then search for candidates, apply filters, and group profiles by job requisition.
This process transforms resumes from unstructured documents into data that hiring systems can work with more reliably.
Limitations of Traditional Resume Parsing
Early resume parsing tools relied heavily on keyword matching and rigid rules. While they reduced manual effort, they introduced new sources of inaccuracy. They are only 60-70% accurate.
Candidates who used different terminology for the same skills were often overlooked. Non-standard resume formats caused incomplete or incorrect data extraction. Ambiguous language was difficult for rule-based systems to interpret. Screening outcomes depended more on resume formatting and phrasing than on actual capability.
These limitations affected both recruiters and candidates. Recruiters faced inconsistent shortlists, while candidates were filtered out for reasons unrelated to job fit. Screening accuracy varied significantly across roles and hiring volumes.
Traditional parsing approaches struggled not because recruiters lacked judgment, but because static systems do not adapt well within complex talent acquisition environments.
How AI Improves Resume Parsing Accuracy
AI-driven resume parsing improves accuracy by interpreting context rather than relying solely on exact matches. AI driven resume parsing improves accuracy by 40%.
Natural Language Processing allows systems to understand variations in language, synonyms, and implied skills. Machine learning models improve extraction accuracy over time by learning from historical hiring data and feedback.
AI parsing performs more reliably across diverse resume formats and non-linear career paths. Candidates with adjacent experience or transferable skills are less likely to be excluded due to phrasing differences or unconventional layouts.
Accuracy improves because resumes are evaluated based on meaning and relevance rather than formatting compliance.
From Resume Parsing to Resume Screening
Resume parsing becomes more valuable when structured data is used to support screening decisions.
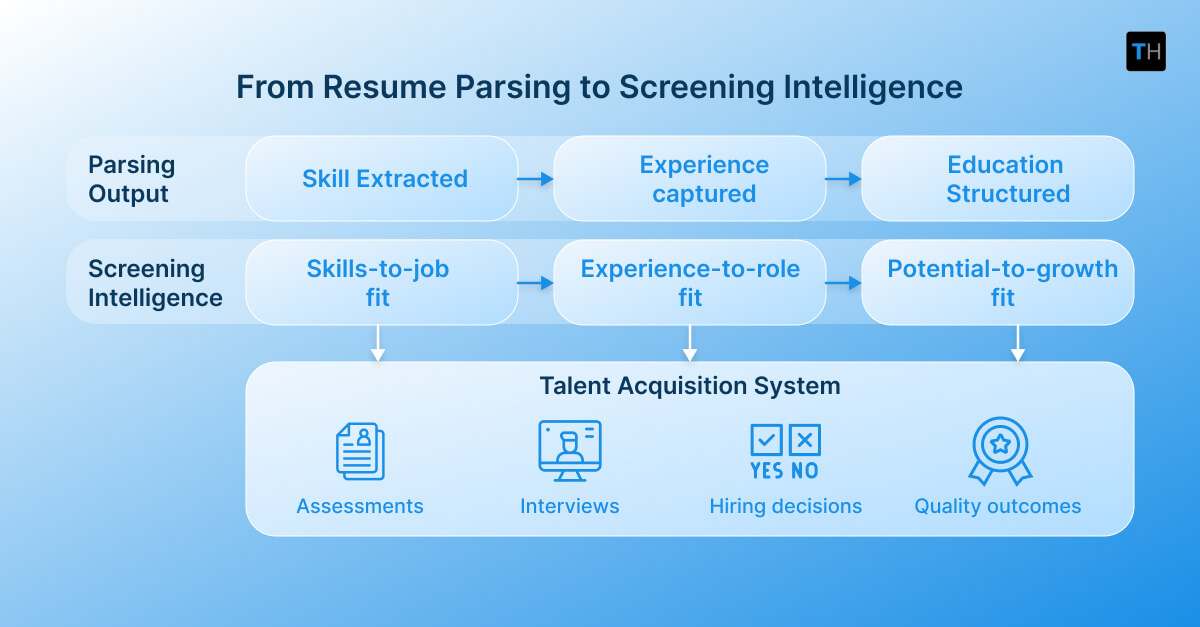
AI-driven resume screening evaluates candidates across multiple dimensions, including:
- Skills-to-job fit, which assesses how relevant a candidate’s skills are to the role requirements
- Experience-to-role fit, which considers tenure, domain exposure, and functional alignment
- Potential-to-growth fit, which identifies transferable skills and adjacent experience
This approach improves shortlist consistency and reduces unnecessary interviews. Recruiters spend less time filtering resumes and more time evaluating candidates who are better aligned with the role.
Screening accuracy becomes more stable across teams, recruiters, and hiring volumes.
Resume Screening Within a Talent Acquisition System
In mature talent acquisition systems, resume screening does not operate as a standalone step.
Screening intelligence connects directly with:
- Job requisition clarity and role definition
- Assessments and interview design
- Hiring decisions and approval workflows
- Quality-of-hire and performance outcomes
Screening functions as an integrated layer that supports downstream decisions rather than acting as an isolated filter. Candidate context flows through the system, reducing rework and repeated evaluation.
This integration allows screening accuracy to scale without increasing recruiter workload.
Impact on Recruiters and Candidates
When resume parsing and screening are implemented as part of a connected system, both recruiters and candidates benefit.
Organizations see more consistent screening outcomes and reduced time to hire. Interview-to-hire ratios improve as interview time is spent on better-aligned candidates. Recruiter fatigue decreases as manual filtering work is reduced.
Candidates receive faster responses and clearer communication, which improves experience and trust early in the process.
Choosing the Right Resume Parsing and Screening Tool
Technology supports hiring outcomes only when it aligns with the broader system.
Effective tools should:
- Integrate closely with job requisition and role definition
- Allow validation and refinement of parsed data
- Support tagging, filtering, and prioritization
- Integrate seamlessly with the ATS
- Balance automation with recruiter judgment
Tools that fragment workflows or require extensive manual reconciliation often reduce accuracy rather than improving it.
Preparing for the Future of Resume Screening
Resume screening continues to evolve alongside changes in hiring complexity.
Emerging capabilities include continuous learning models, inference of soft skills from language patterns, and candidate-centric screening experiences. Screening systems are increasingly expected to adapt to hiring context rather than apply static rules across all roles.
As organizations scale, screening accuracy will depend less on automation volume and more on how well early signals are interpreted and carried forward.
Conclusion
Resume screening shapes who enters the hiring process and how early decisions are made. When screening relies on rigid automation, accuracy and consistency become difficult to sustain at scale. When screening is designed as part of a connected talent acquisition system, it supports better decisions throughout the hiring lifecycle.
Structured resume data, interpreted intelligently and used consistently, improves how candidates are evaluated, how interviews are conducted, and how hiring decisions are made.
TurboHire supports this approach by enabling AI-native, end-to-end talent acquisition systems where resume parsing and screening contribute to decision quality, recruiter effectiveness, and scalable hiring outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is resume parsing in recruitment?
Resume parsing is the process of extracting information from resumes and converting it into structured, searchable data within a hiring system. It allows recruiters and applicant tracking systems to organize candidate details such as skills, experience, and education in a consistent format, making resume screening more efficient and scalable.
2. How does AI improve resume screening accuracy?
AI improves resume screening accuracy by interpreting context rather than relying only on exact keyword matches. It uses natural language processing and machine learning to recognize variations in skills, experience, and phrasing, allowing candidates with relevant but differently expressed qualifications to be evaluated more consistently across roles and hiring volumes.
3. How does resume parsing fit into a talent acquisition system?
Within a talent acquisition system, resume parsing serves as the foundation for early hiring decisions. Structured resume data feeds into screening, assessments, interviews, and hiring outcomes. When integrated properly, resume parsing supports consistent evaluation, reduces manual effort, and improves decision quality across the entire hiring process.



