Time to hire is a cornerstone metric for talent acquisition leaders. It reflects how well the hiring system functions. When time to hire increases, it usually signals deeper structural issues rather than individual performance gaps.
Recruitment automation is often introduced as a way to fix this problem. In practice, automation improves time to hire only when it is applied as part of a connected talent acquisition system.
Speed has become a defining factor in modern hiring. In high-volume hiring environments, candidates do not wait. Delays create uncertainty. Uncertainty leads to disengagement, and the best candidates move on. In fact, top talent is often available for just 10 days; delays beyond this window dramatically increase offer rejection rates.
What Time to Hire Means and Why It Matters in High-Volume Hiring
Defining Time to Hire
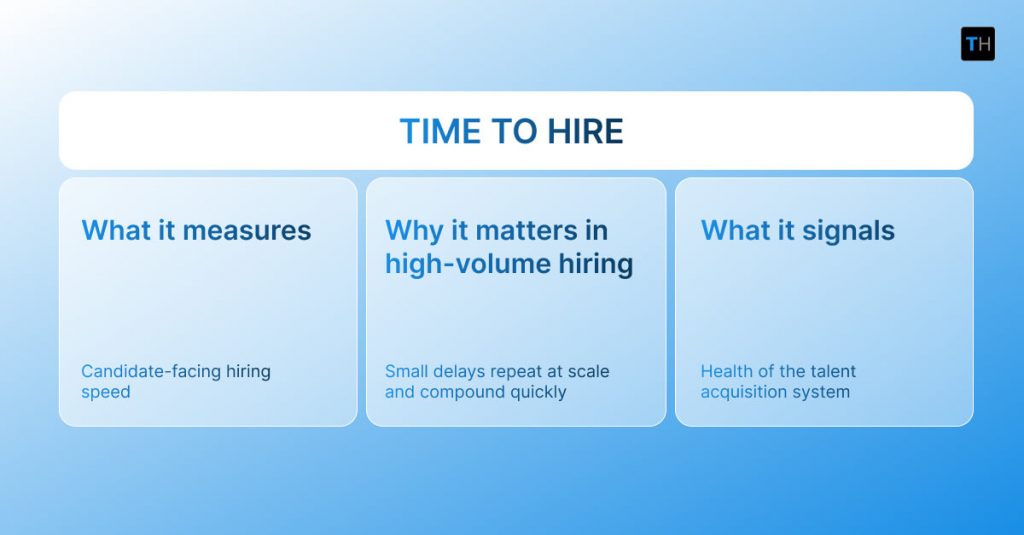
Time to hire measures how long it takes to move a candidate from entry into the hiring process to offer acceptance. It captures candidate-facing speed and reflects how efficiently the organization evaluates and decides.
In high-volume hiring, this metric matters because small delays repeat at scale. What feels manageable for one role becomes a bottleneck across dozens.
How Time to Hire Is Calculated
Time to hire is calculated as:
Date of offer acceptance minus date of candidate application or sourcing
The exact start point matters less than consistency. What leaders need is a reliable signal of how quickly candidates progress once they enter the system.
Why Long Time to Hire Hurts Hiring Outcomes at Scale
Costs rise as recruiters spend more time coordinating and reworking pipelines. Strong candidates exit early in competitive markets. Short-staffed teams result in slow delivery and dwindling revenue.
Delays stack across teams and roles. Recruiters shift from strategic evaluation to reactive firefighting. The system becomes harder to control as volume increases.
A long time to hire rarely comes from one broken step. It comes from friction spread across the entire talent acquisition system.
Where Traditional Hiring Approaches Break Down

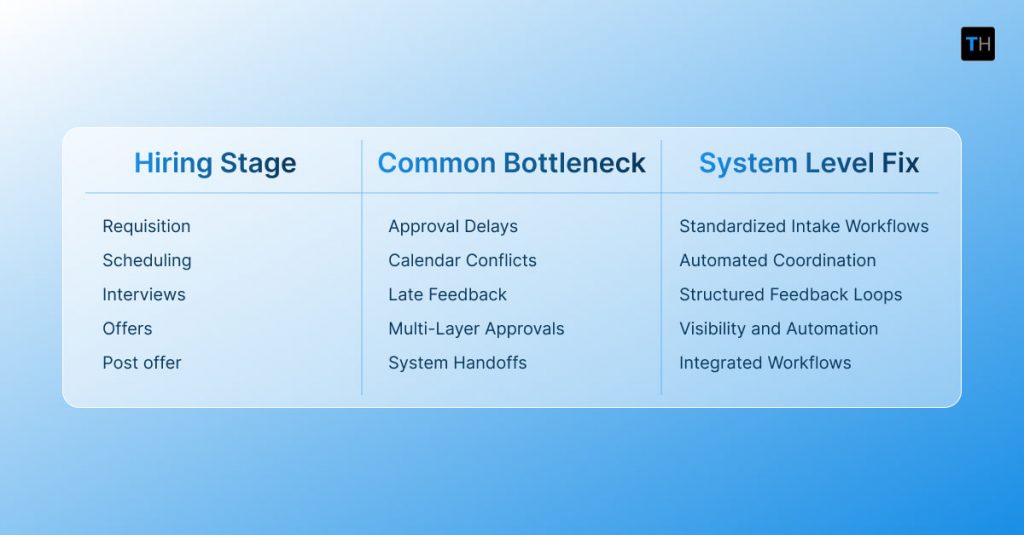
Common points of failure include manual resume screening, interview scheduling across multiple calendars, inconsistent candidate communication, and delayed feedback. Decision-making often slows when ownership is unclear. Disconnected tools further fragment data and visibility.
This is not a recruiter effort issue. It is a system coordination issue.
Why Recruitment Automation Often Fails to Reduce Time to Hire
Recruitment automation is frequently applied in pieces. Teams automate tasks rather than fixing the flow. In spite of record investment in HR technology, the global average time-to-hire rose to 44 days in 2025 from 31 days in 2024.
A new tool speeds up scheduling. Another improves sourcing. Yet approvals still stall. Feedback arrives late. Offers wait on multiple sign-offs. Activity increases but cycle time does not meaningfully improve.
In some cases, automation accelerates early stages and creates congestion later. Candidates move quickly at first, then wait. Recruiters feel busier, but hiring velocity remains unchanged.
Recruitment automation reduces time to hire only when it strengthens the talent acquisition system as a whole.
How Recruitment Automation Done Right Improves Time to Hire Systemically
Recruitment automation works when it restores end-to-end flow across high-volume hiring systems.

1. Requisition and Intake
Standardized intake and approval workflows reduce delays at the start. A clear role context prevents rework later.
2. Sourcing and Pipeline Continuity
Continuous sourcing and candidate rediscovery keep pipelines active. Recruiters rely less on reactive hiring and last-minute sourcing.
3. Screening and Shortlisting
Structured screening improves early throughput. Automation helps reduce noise while preserving recruiter judgment.
4. Communication and Scheduling
Automated coordination removes calendar bottlenecks. Candidates move through stages without unnecessary waiting.
5. Interviews and Feedback
Structured interview workflows and centralized feedback reduce decision latency. Hiring managers know what input is required and when.
6. Offers and Closures
Faster approvals and streamlined offer workflows preserve candidate momentum. Drop-offs decrease when timelines are predictable.
7. System Integration
Integration with HRMS, payroll, and background verification systems prevents delays after offers are made. Handoffs become seamless rather than disruptive. System integrations is one of the top barriers when it comes to hiring automation.
No single feature improves time to hire on its own. Hiring velocity improves when the system moves smoothly from start to finish.
Challenges in Automating High-Volume Hiring Using Recruitment Automation
Recruitment automation introduces risks when applied without system thinking.
- Over-automation can damage candidate experience if relevance declines.
- Poor filters can exclude strong candidates.
- Change management becomes critical as workflows evolve.
- Data privacy and compliance must remain consistent at scale.
- Integration complexity can introduce new friction if systems remain fragmented.
- Automation amplifies existing processes. Without a strong design, it amplifies inefficiency.
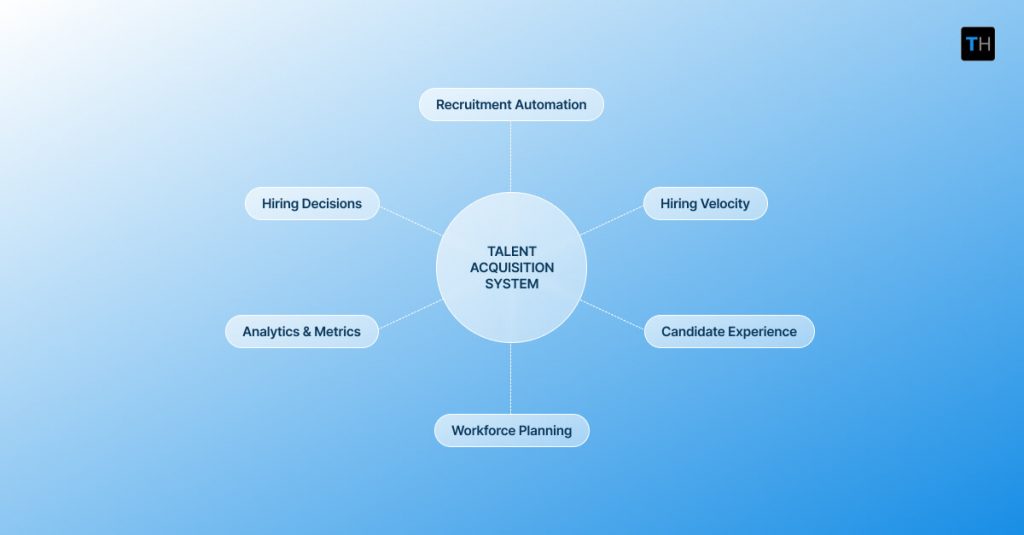
Key Components of Recruitment Automation in a Talent Acquisition System
Recruitment automation reduces time to hire only when its components work together as part of a unified system. Isolated features create activity. Integrated capabilities create flow.
The following components matter not because they exist, but because of how they support coordination, visibility, and decision-making across the hiring lifecycle.
1. Native AI for System Intelligence
Native AI supports prioritization and signal detection across the hiring system. It helps surface relevant candidates, highlights stalled pipelines, and supports recruiter decision-making.
2. Applicant Tracking System (ATS)
An ATS provides the structural backbone of recruitment automation. It ensures consistency in workflows, maintains hiring context across stages, and creates a single source of truth for candidates, roles, and decisions.
3. Resume Parsing and Structured Screening
Resume parsing and screening capabilities reduce early-stage noise. By structuring candidate data and applying consistent criteria, recruiters spend less time filtering and more time evaluating.
4. Automated Scheduling
Scheduling automation removes one of the most common sources of delay in high-volume hiring. It coordinates availability across recruiters, hiring managers, and candidates to prevent idle time between stages and preserves candidate momentum.
5. Automated Communication
Automated communication ensures candidates receive timely updates, reminders, and follow-ups. When used thoughtfully, it improves clarity and consistency without turning hiring into a transactional experience.
6. CRM Capabilities Beyond Candidate Storage
Recruitment CRMs support relationship-building at scale. Lead scoring, talent pooling, and engagement tracking help teams prioritize candidates and maintain pipeline continuity. This reduces reactive hiring and improves time to hire over repeated cycles.
7. Chatbots and AI Assistants
Chatbots and AI assistants support high-volume candidate interactions by handling common queries, collecting information, and guiding candidates through early steps. They reduce recruiter load while maintaining responsiveness.
8. Integration Workflows Across Systems
Integration workflows connect recruitment automation with HRMS, payroll, background verification, and other peripheral systems. These integrations prevent handoff delays, eliminate duplicate data entry, and ensure continuity after offer acceptance.
9. Integrated Pipeline and Analytics
Pipeline visibility and analytics reveal where time is being lost. By tracking movement, drop-offs, and stage-level delays, teams can identify systemic bottlenecks and improve hiring velocity over time.
Best Practices for Using Recruitment Automation to Reduce Time to Hire
Effective automation follows a few core principles:
- Map the current hiring system to identify real bottlenecks.
- Define clear goals tied to time to hire and time to fill.
- Automate coordination before automating decisions.
- Scale gradually and validate impact at each stage.
- Enable recruiters and hiring managers through training.
- Use candidate experience or offer acceptance as guardrails.
- Monitor flow continuously and adjust the system.
The goal is not to move faster at all costs. The goal is to move consistently and predictably.
Conclusion: Time to Hire Reflects System Design
A long time to hire is not a recruiter’s problem. It is a system problem.
Recruitment automation improves hiring speed when it strengthens the talent acquisition system. When coordination is automated, and judgment remains human, high-volume hiring becomes faster without losing quality or trust.
TurboHire enables end-to-end recruitment automation designed to improve time to hire by supporting talent acquisition as a connected system.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is recruitment automation in talent acquisition?
Recruitment automation refers to using technology to reduce manual coordination across the hiring process, such as requisition approvals, candidate communication, interview scheduling, and feedback collection. In talent acquisition, automation works best when it supports the system as a whole rather than replacing recruiter judgment or decision-making.
2. How does recruitment automation reduce time to hire?
Recruitment automation reduces time to hire by removing delays between hiring stages. It improves coordination across sourcing, screening, scheduling, feedback, and offer workflows. When applied systemically, automation restores flow across the talent acquisition process instead of speeding up isolated steps.
3. Why is time to hire critical in high-volume hiring?
In high-volume hiring, small delays repeat at scale. A long time to hire leads to higher candidate drop-off, lower offer acceptance, and increased hiring costs. It also signals breakdowns in the talent acquisition system, not just issues with recruiter workload.